Infertility and IVF
Infertility and In Vitro Fertilization
One out of every 10 couples suffers from infertility, (the failure to achieve pregnancy within one year of regular unprotected sexual intercourse). The cause of infertility may vary, however generally speaking one third of the cases can be attributed to the male and the other one third to the female, the remaining third can be due to both male and female. Finally in 10 to 15% of infertility cases a cause cannot be identified (Unexplained infertility).
The assessment of the infertile couple includes a series of standard diagnostic tests. Occasionally (depending on the individual needs of the couple) more comprehensive and specialized tests may be necessary. Standard tests include, (besides a detailed clinical exam), an ultrasound, baseline hormone values, hysterosalpingography, semen analysis, and occasionally laparoscopy and/or hysteroscopy. This assessment will reveal the source of the problem along with the most appropriate means of resolving it.
Generally, depending on the cause of infertility the treatment may be surgical (fibroids, endometriosis, congenital defects), or via some type of assisted reproduction techniques ( ART) such as (ovarian stimulation, intra uterine insemination (IUI), or in vitro fertilization (IVF).
In Vitro Fertilization (IVF)
IVF is a technique used for couples that have not been able to conceive with other less complex methods or when there are severe problems with the sperm or the fallopian tubes.
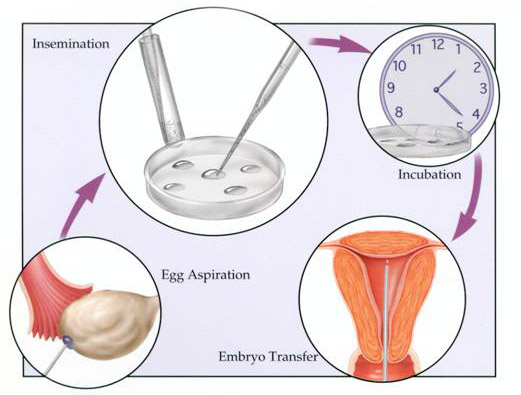
Five separate steps must be completed with success in order for IVF to result in a healthy pregnancy
- Ovarian stimulation via the use of hormones in order to achieve the development of an adequate number of eggs.
- Collection of the mature eggs from the ovary
- Fertilization of the eggs with sperm from the husband or donor (when appropriate) in the IVF lab.
- Transfer of the viable embryos to the womb
- Normal embryo development in the womb
In the event that even one of the above steps isn’t successful it is impossible for pregnancy to be achieved.
1. Ovarian Stimulation via the use of hormones (gonadotropins)
Generally, there must be a sufficient number of eggs in order to begin the process of IVF . Through the use of gonadotropins that are administered for two to three weeks, (depending on the protocol that is followed) the ovaries are stimulated in order to produce multiple follicles. The development of the follicles is monitored by measuring estrogen levels in the woman’s blood stream. Also, transvaginal ultrasounds are performed regularly in order to monitor-measure the development of the follicles.
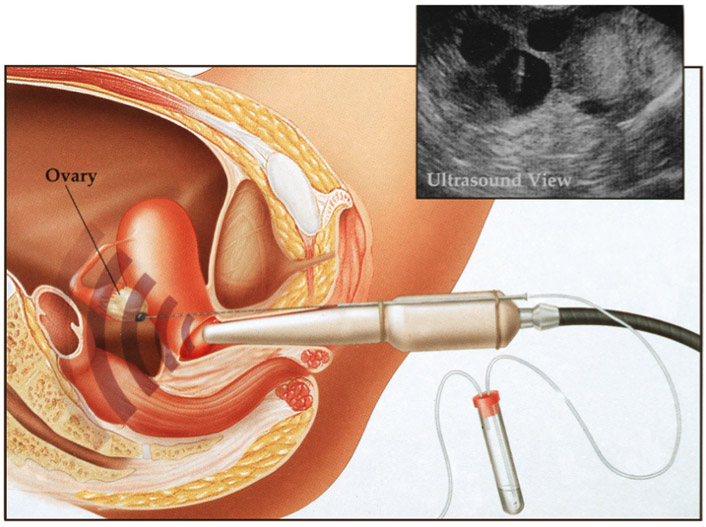
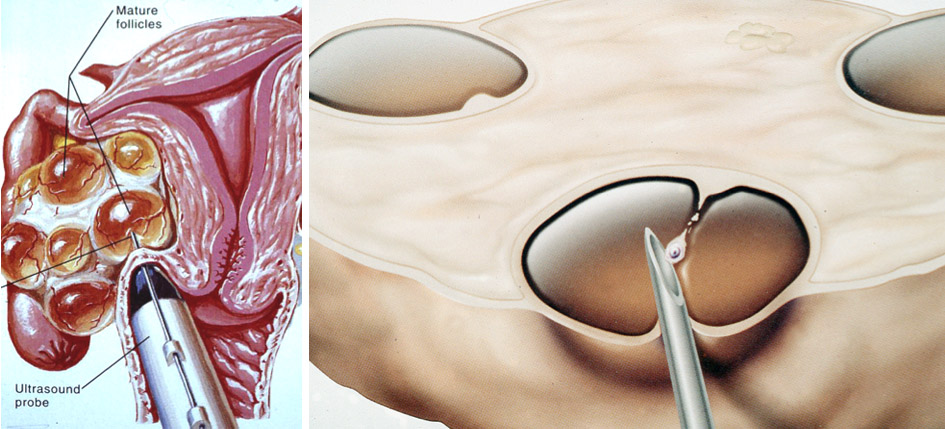
2. Ova Collection
When the follicles reach a certain size (approx. 17 mm) the eggs contained within the follicles are collected and transferred to the lab in order to be fertilized with the partners sperm. Under sonographic guidance, a needle is inserted via the vagina into each follicle and the fluid containing the egg is aspirated with a suction device. This process is completed under light anesthesia in a surgical setting. The fluid is transferred to the lab and the eggs are separated and placed individually in specialized plates.
3. Fertilization of the eggs
On the day of egg collection, the sperm that is intended for fertilization is collected from the male companion via masturbation. The sperm is processed and the eggs are inseminated in an incubation chamber. Usually 50-70% of the eggs will fertilized and they will be allowed to develop as embryos in the lab for the next 3 to 5 days.
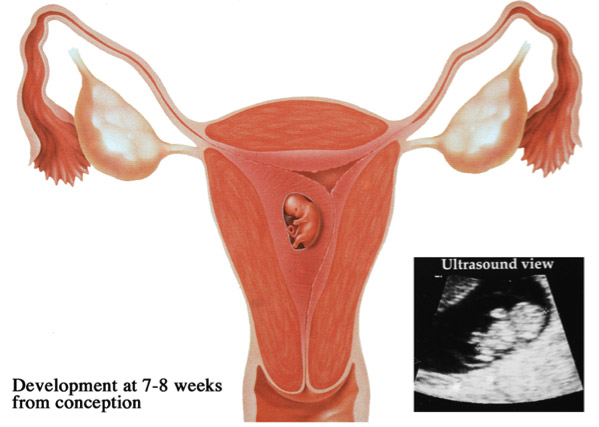
4. Embryo Transfer to the womb
Three to five days after insemination the fertilized eggs have progress into embryos. Typically two for these developing embryos are selected and transferred with a special catheter into the womb. The remaining embryos are frozen in order to be used at a later time if needed. Under sonographic guidance, a fine plastic catheter that contains the embryos, is passed through the cervix into the cavity of the womb. Then the the embryos are released together with a few drops of nutrient rich liquid. The process only lasts for a few minutes and is usually painless. The patients need to remain at home for the next 72 hours and avoid any activity. A blood pregnancy test is performed 12 days after the embryo transfer.
5. Implantation of the embryos and their further development
During the natural process of fertilization, early implantation of the embryos is effected by the corpus luteum, which is a small progestrone producing cyst. In IVF during the process of egg collection the follicles are suctioned, and the natural function of the corpus luteum may be inhibited. In order to facilitated the development of the endometrium during the embryo transfer , following the surgical collection of the eggs, progesterone along with estrogen are administered.
Al patients involved in any type of assisted fertility program must understand that the success rate of IVF relies primarily on their age as well as the cause of infertility. A typical fertile couple has about a 25% chance of conceiving with unprotected sexual encounters during the span of one month. Pregnancy rates after IVF are mainly related to the age of the women in the range between 35 to 50%. Also, it must be noted that some couples cannot complete the process due to a lack response to the treatment or lack of fertilization. If this occurs, an
appointment must be arranged with the Dr in order to discuss potential causes and a modification of treatment protocol.

