Human Papiloma Virus
(Human papillomavirus-HPV) is a DNA VIRUS that belongs to the papillovirus family and is capable of infecting humans.
More than 30-40 types of the HPV virus may be transmitted via sexual intercourse, infecting the anogenital area. Some of the sexually transmittable forms of HPV may cause genital warts (typically low risk). Persistent infection by (high risk HPV strains, which are different than the types that cause warts) may evolve into pre cancerous lesions and or infiltrative cancer. HPV is solely responsible for most cases of cervical cancer. However, most HPV infections do not automatically cause disease in fact usually they resolve on their own.
Seventy percent of HPV infections in young people may resolve on their own within one year and 90% may resolve within 2 years. However, when the subclinical infection persists (relevant to 5% - 10% of infected women) that the risk for developing precancerous lesions of the cervix that may develop into infiltrative cervical cancer is quite high.
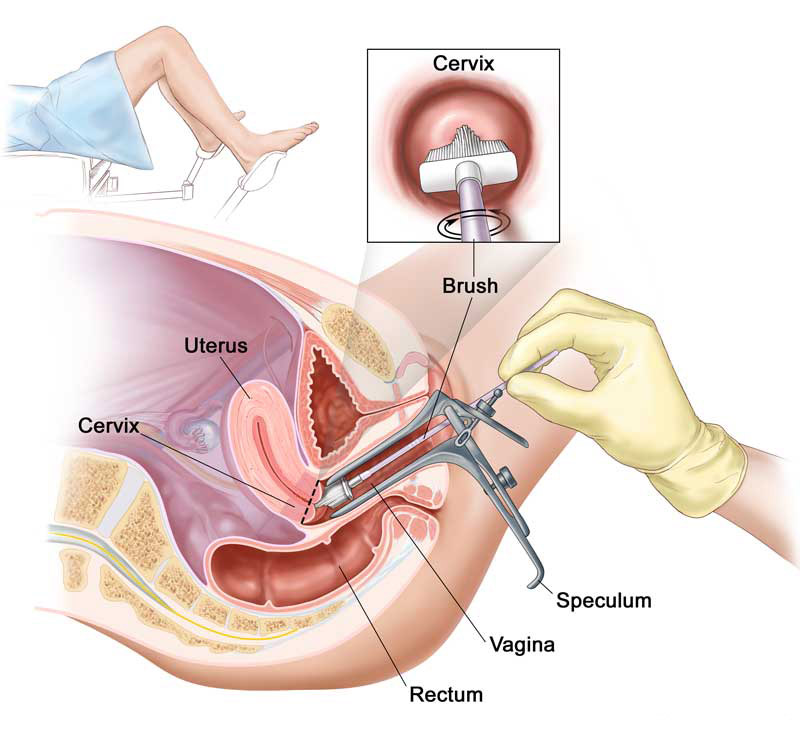
Test Pap
The time lapse between sub clinical infection (without lesions) to clinical infection (detectable via pap smear) may be years long, allowing the woman the opportunity to detect and cure the pre cancerous lesions. Progress to infiltrative cancer may be prevented when the sub clinical infection is detected early via routine pap smears.
The Pap Smear aids in the inspection of the cervix for abnormal cells that may evolve into cancer
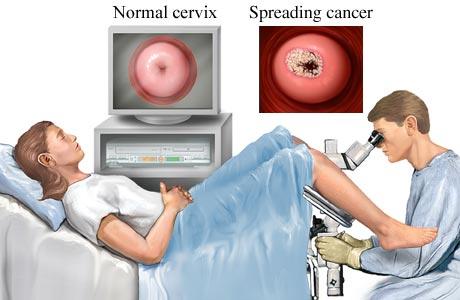
Colposcopy
If abnormal cells are found during the pap smear than a colposcopy is performed. A colposcopy is a simple process in which the cervix is examined under a microscope. Specialized pigments are used in order to detect areas of the cervix that look suspicious for malignancy. If deemed necessary biopsies may be taken for further examination.
Lately HPV typing is used in combination with the pap smear in order to offer a more accurate diagnostic tool, making it easier to monitor women and thus offering efficacy in cervical cancer prevention.
The assessment of the cervix must take place on a yearly basis, beginning at the age of 18 or alternatively one year after the beginning of sexual activity.
Treatment
There is no specialized treatment for HPV viral infection at this
time. However the viral infection does resolve itself most of the time,
According to the CDC the immune system may combat the infection up to
90% of the time within two years.. Basic prerequisite for the
elimination of the virus is smoking cessation, as smoking has been found
to lower the body’s local defenses, it has been linked directly to HPV
infection. However specialists cannot agree on whether the virus is
eliminated or just not detectable, therefore it is difficult to know
when in fact the virus is contagious..
The electrosurgical excision procedure (LEEP) is one of the most often used procedures for the treatment of high grade lesions of the cervix (CIN II/CIN III, HGIL). As aforementioned lesions are detected via pap smear or colposcopy. In the United Kingdom this procedure is known as large loop excision of the transformation zone (LLETZ). The procedure has many advantages, low cost, high success rate and easy use.
Complications are less frequent in comparison to the (cold knife conization), however, they may include infection and hemorrhage.
The scars of the cervix can theoretically cause problems in conception. However a large study showed that the LEEP procedure did not have an effect on fertility.

